1. 상속을 UML로 표기해 보세요.
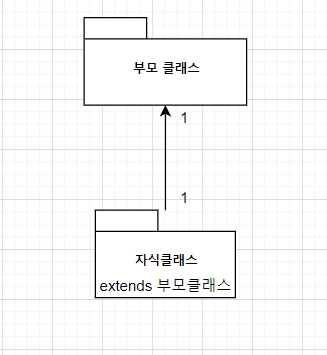
2. 부모클래스와 자식클래스의 다른 용어들은?
- 부모 클래스: 상위 클래스, 슈퍼 클래스
- 자식 클래스: 하위 클래스, 서브 클래스
3. super 키워드와 this 키워드의 차이는 무엇인가요?
| super | this |
| 부모클래스를 참조한다. | 자기 자신(생성자)을 참조한다. |
class SuperCLS { // 부모 클래스
private int superVar;
public SuperCLS(int superVar) {
this.superVar = superVar
}
}
class SubSLS extends SuperCLS { // 자식 클래스
private int subVar;
public SubCLS(int superVar, int subVar) {
super(superVar); // super 키워드를 통해 부모 클래스의 멤버 변수를 불러올 수 있다.
this.subVar = subVar; // this 키워드를 통해 자기 자신(생성자)의 멤버 변수를 선언할 수 있다.
}
}4. 단일 상속과 다중상속 이란?
- 단일 상속: 부모 클래스와 자식 클래스가 1 : 1 관계로 이루어진 상속을 의미한다. 같은 구문이 두 가지 이상의 의미로 해석될 여지가 있어서는 안 되는 프로그래밍의 기법을 준수한다.
- 다중 상속: 부모 클래스와 자식 클래스가 1 : n (or) n : 1 (or) n : m의 관계로 이루어진 상속을 의미한다. 다중 상속은 다이아몬드 문제로 인해 Java에서는 쓰이지 않는 기법이다.
- (※ 다이아몬드 문제: 다중 상속 받은 자식 클래스가 어느 부모의 메소드를 따라야 하는지 명확히 발생되지 않는 현상. UML로 표기시 마치 다이아몬드의 형태와 비슷하다 하여 명명됨)
5. 다음 코드와 같이 과목과 점수가 짝을 이루도록 2개의 배열을 작성하라.
String course[] = {"Java", "C++", "HTML5", "컴퓨터구조", "안드로이드"};
int score[] = {95, 88, 76, 62, 55};그리고 다음 예시와 같이 과목 이름을 입력받아 점수를 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하라. “그만”을 입력받으면 종료한다. (Java는 인덱스 0에 있으므로 score[0]을 출력)
과목 이름 » Jaba
없는 과목입니다.
과목 이름 » Java
Java의 점수는 95
과목 이름 » 안드로이드
안드로이드의 점수는 55
과목 이름 » 그만
[Hint] 문자열을 비교하기 위해서는 String 클래스의 equals()메소드를 이용해야 한다.String name;
if(course[i].equals(name)) {
int n = score[i];
...
}
5-1. 과목 및 점수 클래스
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GradesMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String course[] = {"Java", "C++", "HTML5", "컴퓨터구조", "안드로이드"};
int score[] = {95, 88, 76, 62, 55};
String name;
int i = 0;
while (true) {
System.out.println("과목이름>>");
name = scanner.next();
if (name.equals("그만")) {
break;
}
for (i = 0; i < course.length; i++) {
if (course[i].equals(name)) {
System.out.println(course[i] + "의 점수는 " + score[i]);
break;
}
}
if (i == course.length) {
System.out.println("없는 과목입니다.");
}
}
scanner.close();
}
}6. 다음은 2차원 상의 한 점을 표현하는 Point 클래스이다.
class Point {
private int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
protected void move(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}Point를 상속받아 색을 가진 점을 나타내는 ColorPoint 클래스를 작성하라. 다음 main() 메소드를 포함하고 실행 결과와 같이 출력되게 하라.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(5, 5, "YELLOW");
cp.setXY(10, 20);
cp.setColor("RED");
String str = cp.toString();
System.out.println(str + " 입니다. ");
}> RED색의 (10,20)의 점입니다.6-1. 메인 클래스
public class MyColorPoint {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(5, 5, "YELLOW");
cp.setXY(10, 20);
cp.setColor("RED");
String str = cp.toString();
System.out.println(str + " 입니다.");
}
}6-2. Point 클래스(부모 클래스)
public class Point {
private int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x; this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
protected void move(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}6-3 ColorPoint 클래스(자식 클래스)
public class ColorPoint extends Point {
private String color;
public ColorPoint(int x, int y, String color) {
super(x, y);
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setXY(int x, int y) {
move(x, y);
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String toString() {
return this.color + "색의 ("+ getX() + ", " + getY() + ") 점";
}
}7. Point를 상속받아 색을 가진 점을 나타내는 ColorPoint 클래스를 작성하라. 다음 main() 메소드를 포함하고 실행 결과와 같이 출력되게 하라.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint zeroPoint = new ColorPoint(); // (0,0) 위치의 BLACK 색 점
System.out.println(zeroPoint.toString() + "입니다.");
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(10, 10); // (10,10) 위치의 BLACK 색 점
cp.setXY(5,5); cp.setColor("RED");
System.out.println(cp.toString()+"입니다.");
}> BLACK색의 (0,0) 점입니다. RED색의 (5,5) 점입니다.7-1. 메인 클래스
public class MyColorPoint {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ColorPoint zeroPoint = new ColorPoint(); // (0,0) 위치의 BLACK 색 점
System.out.println(zeroPoint.toString() + "입니다.");
ColorPoint cp = new ColorPoint(10, 10); // (10,10) 위치의 BLACK 색 점
cp.setXY(5,5); cp.setColor("RED");
System.out.println(cp.toString()+"입니다.");
}
}7-2 Point 클래스(부모 클래스)
public class Point {
private int x, y;
public Point() {
this(0, 0);
}
public Point(int x, int y) { }
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
protected void move(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}7-3. ColorPoint 클래스(자식 클래스)
public class ColorPoint extends Point {
private String color;
public ColorPoint() {
super();
this.color = "BLACK";
}
public ColorPoint(int x, int y) {
super(x, y);
}
public ColorPoint(int x, int y, String color) {
super(x, y);
this.color = color;
}
public void setXY(int x, int y) {
move(x, y);
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String toString() {
return this.color + "색의 ("+ getX() + ", " + getY() + ") 점";
}
}8. Point를 상속받아 3차원의 점을 나타내는 Point3D 클래스를 작성하라. 다음 main() 메소드를 포함하고 실행 결과와 같이 출력되게 하라.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point3D p = new Point3D(1,2,3); // 1,2,3은 각각 x, y, z축의 값.
System.out.println(p.toString()+"입니다.");
p.moveUp(); // z 축으로 위쪽 이동
System.out.println(p.toString()+"입니다.");
p.moveDown(); // z 축으로 아래쪽 이동
p.move(10, 10); // x, y 축으로 이동
System.out.println(p.toString()+"입니다.");
p.move(100, 200, 300); // x, y, z축으로 이동
System.out.println(p.toString()+"입니다.");
} > (1,2,3) 의 점입니다.
> (1,2,4) 의 점입니다.
> (10,10,3) 의 점입니다.
> (100,200,300) 의 점입니다.8-1. 메인 클래스
public class MyColorPoint {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point3D p = new Point3D(1, 2, 3); // 1,2,3은 각각 x, y, z축의 값.
System.out.print(p.toString()+"입니다.");
System.out.println(" : 초기점");
p.moveUp(); // z 축으로 위쪽 이동
System.out.print(p.toString()+"입니다.");
System.out.println(" : 첫 번째 이동");
p.moveDown(); // z 축으로 아래쪽 이동
p.move(10, 10); // x, y 축으로 이동
System.out.print(p.toString()+"입니다.");
System.out.println(" : 두 번째 이동");
p.move(100, 200, 300); // x, y, z축으로 이동
System.out.print(p.toString()+"입니다.");
System.out.println(" : 마지막 이동");
}
}8-2. Point 클래스(부모 클래스)
public class Point {
private static int x, y, z;
public Point(int x, int y, int z) {
Point.x = x; Point.y = y; Point.z = z;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public int getZ() {
return z;
}
public void moveUp() {
Point.z = z + 1;
}
public void moveDown() {
Point.z = z - 1;
}
public void move(int x, int y) {
Point.x += x;
Point.y += y;
}
public void move(int x, int y, int z) {
Point.x += x;
Point.y += y;
Point.z += z;
}
}8-3. Point3D 클래스(자식 클래스)
public class Point3D extends Point {
public Point3D(int x, int y, int z) {
super(x, y, z);
}
public String toString() {
return "(" + getX() + ", " + getY() + ", " + + getZ() + ")" + "의 점";
}
}9.배열을 이용하여 간단한 극장 예약 시스템을 작성하여 보자.
아주 작은 극장이라서 좌석이 10개 밖에 되지 않는다.
사용자가 예약을 하려고 하면 먼저 좌석 배치표를 보여준다.
즉, 예약이 끝난 좌석은 1로, 예약이 되지 않은 좌석은 0으로 나타낸다.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
--------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
몇번째 좌석을 예약 하시겠습니까? 2
--------------------
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
--------------------
0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
9-1. 메인 클래스
public class ReservationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Reservation reservation = new Reservation();
reservation.show();
}
}9-2. 극장 예약 알고리즘 클래스
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Reservation {
private int num;
static private int[] sit;
public Reservation() {
sit = new int[10];
}
public Reservation(int num, int[] sit) {
this.num = num;
Reservation.sit = sit;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public void setNum(int num) {
this.num = num;
}
public int[] getSit() {
return sit;
}
public void setSit(int[] sit) {
Reservation.sit = sit;
}
public int getCinema() {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("몇 번째 좌석을 예약 하시겠습니까?: ");
int num = scanner.nextInt();
sit[num] = num;
scanner.close();
return sit[num];
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 : 좌석 번호");
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < sit.length; i++) {
System.out.print(sit[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
getCinema();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 : 좌석 번호");
System.out.println("-------------------");
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < sit.length; i++) {
if (sit[i] != 0) {
System.out.print(1 + " ");
} else {
System.out.print(sit[i] + " ");
}
}
}
}'WebDev > 본과정' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 객체 비교와 인터페이스 (0) | 2021.05.12 |
|---|---|
| 다형성과 오버라이딩 (0) | 2021.05.12 |
| 배열의 탐색 및 정렬 (0) | 2021.05.12 |
| String 클래스의 메소드 및 배열 기초 (0) | 2021.05.12 |
| 오버로딩과 String (0) | 2021.05.11 |




최근댓글