1. Marker 인터페이스에 대하여 설명하시오.
: 클래스에 특정 표시를 해두기 위한 목적으로 정의된 인터페이스를 지칭한다.
interface Upper { } // Marker 인터페이스에는 구현해야할 메소드가 없는 경우가 흔하다.
interface Lower { } interface Printable { // 일반적인 형태의 인터페이스
String getContents();
}
class Report implements Printable, Upper { // Marker 인터페이스로 인해 클래스 별로 분류되는 기능을 가질 수 있다.
String cons;
Report(String cons) {
this.cons = cons;
}
public String getContents() {
return cons;
}
}
class ReportMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String cons = "";
Report report = new Report(cons);
if (cons instanceof Upper) { // instanceof로 해당 인터페이스에게 implements 되었는지 확인할 수 있다.
System.out.println(cons.toUpperCase());
} else if (cons instanceof Lower) {
System.out.println(cons.toLowerCase());
}
}
}2. 추상클래스에 대하여 설명하시오.
: 하나 이상의 추상(abstract 키워드가 붙은) 메소드를 지니는 클래스를 의미한다.
public abstract class House { // 추상 클래스를 대상으로 인스턴스 생성이 불가능 하지만, 참조변수 선언은 가능하다.
public abstract void method(); // 추상 메소드. 인터페이스처럼 구현부(Body)가 없는 것이 특징이다.
}3. 추상클래스와 인터페이스의 차이는?
| 추상클래스(Abstract Class) | 인터페이스(Interface) |
| 단일 상속(extends)만 가능하다. | 다중 구현(implements)이 가능하다. |
4. 에러와 예외의 차이는?
| 에러(Error) | 예외(Exception) |
| 시스템 상 비정상적인 상황(메모리가 차거나 손상된 경우) | 비정상적인 코드로 인해 발생하는 상황 |
5. unchecked 와 cheked 예외의 차이는?
| unchecked | checked |
| JVM에 의해 런타임시 발생하는 에러처리 | 런타임 전 발생하는 에러처리 |
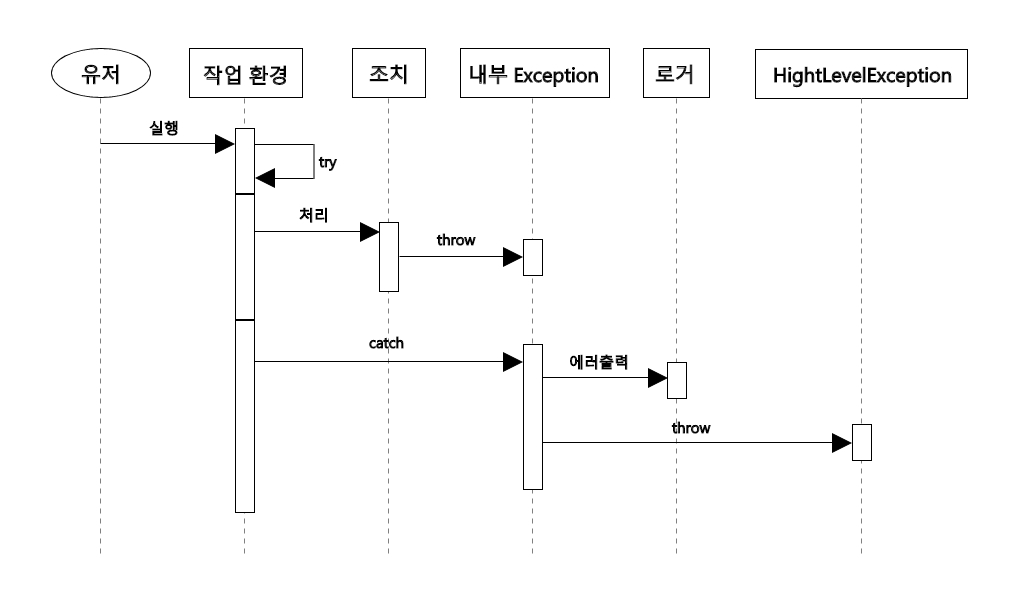
6. 예외처리 시퀀스 다이어그램을 그리시오.
7. 사칙연산 계산기를 아래의 조건으로 짜시오.
- interface 를 활용할것
- 예외처리 메커니즘을 적용할것.
7-1. 메인 클래스
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CalMain { // CalMain에서 Calculator 테스트하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Calculate cal = new Calculator();
System.out.println("계산할 정수 두 개를 띄어써서 입력해주세요.");
System.out.println("ex) 3 4");
try {
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int y = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println(cal.add(x, y));
System.out.println(cal.sub(x, y));
System.out.println(cal.mul(x, y));
System.out.println(cal.div(x, y));
} catch (Exception e) { // 정수가 아닌 값을 입력하거나, 올바르지 않은 연산 값(분모가 0인)을 입력할 때
System.out.println("올바르지 않은 입력 값 입니다!"); // 오류 메시지 출력
}
scanner.close();
}
}7-2. Calculate 인터페이스
public interface Calculate {
int add(int x, int y);
int sub(int x, int y);
int mul(int x, int y);
int div(int x, int y);
}7-3. Calculator 클래스(implements Calculate)
public class Calculator implements Calculate {
@Override
public int add(int x, int y) {
return x + y;
}
@Override
public int sub(int x, int y) {
return x - y;
}
@Override
public int mul(int x, int y) {
return x * y;
}
@Override
public int div(int x, int y) {
return x / y;
}
}8. 다음 Stack 인터페이스를 상속받아 실수를 저장하는 StringStack 클래스를 구현하라.
interface Stack {
int length(); // 현재 스택에 저장된 개수 리턴
int capacity(); // 스택의 전체 저장 가능한 개수 리턴
String pop(); // 스택의 톱(top)에 실수 저장
boolean push(String val); // 스택의 톱(top)에 저장된 실수 리턴
}그리고 다음 실행 사례와 같이 작동하도록 StackApp 클래스에 main() 메소드를 작성하라.
> 총 스택 저장 공간의 크기 입력 >> 3
> 문자열 입력 >> hello
> 문자열 입력 >> sunny
> 문자열 입력 >> smile
> 문자열 입력 >> happy
> 스택이 꽉 차서 푸시 불가!
> 문자열 입력 >> 그만
> 스택에 저장된 모든 문자열 팝 : smile sunny hello8-1. 메인 클래스
import java.util.Scanner;
public class StackMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int size = 0;
System.out.print("총 스택 저장 공간의 크기 입력 >> ");
try {
size = scanner.nextInt();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("올바르지 않은 입력 값 입니다. 다시 입력해주세요!");
}
StackApp stack = new StackApp(size);
for (int i = 0; i < stack.capacity(); i++) {
System.out.print("문자열 입력 >> ");
String str = scanner.next();
if (str.equals("그만"))
break;
stack.push(str);
}
stack.printStack();
scanner.close();
}
}8-2. Stack 인터페이스
public interface Stack {
int length(); // 현재 스택에 저장된 개수 리턴
int capacity(); // 스택의 전체 저장 가능한 개수 리턴
String pop(); // 스택의 톱(top)에 실수 저장
boolean push(String val); // 스택의 톱(top)에 저장된 실수 리턴
}8-3. StringStack 클래스 (implements Stack)
public class StackApp implements Stack {
private int top; // 스택의 맨 위 부분
private int size; // 입력할 저장 공간의 크기를 입력할 수
private String str[]; // 입력할 문자열을 담는 객체
public StackApp(int size) {
top = -1;
this.size = size;
str = new String[this.size];
}
@Override
public int length() { // 현재 스택에 저장된 개수 리턴
return top;
}
@Override
public int capacity() { // 스택의 전체 저장 가능한 개수 리턴
return size;
}
@Override
public String pop() { // 스택의 톱(top)에 스트링을 pop
if (length() == -1)
System.out.println("스택에 데이터가 없습니다!");
return str[--top]; // LIFO 형태에 따라 top 부터 pop
}
@Override
public boolean push(String pustr) { // 스택의 톱(top)에 스트링을 push
if (top == (this.size - 1)) {
System.out.println("스택이 꽉 차서 푸시 불가!");
return false;
} else {
str[++top] = pustr; // 다음 스택 포인터가 가리키는 인덱스에 데이터 추가
}
return true;
}
public void printStack() { // 스택에 저장된 모든 문자열 출력
if (length() == -1) {
System.out.println("스택에 데이터가 없습니다!");
} else {
System.out.print("스택에 저장된 모든 문자열 팝 : ");
for (int i = 0; i <= top; i++) {
System.out.print(str[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}9. 철수 학생은 다음 3개의 필드와 메소드를 가진 4개의 클래스 Add, Sub, Mul, Div를 작성하려고 한다.
- int 타입의 a, b 필드: 2개의 피연산자
- void setValue(int a, int b): 피연산자 값을 객체 내에 저장한다.
- int calculate(): 클래스의 목적에 맞는 연산을 실행하고 결과를 리턴한다.
- 곰곰 생각해보니, Add, Sub, Mul, Div 클래스에 공통된 필드와 메소드가 존재하므로 새로운 추상 클래스 Calc를 작성하고 Calc를 상속받아 만들면 되겠다고 생각했다. 그리고 main() 메소드에서 다음 실행 사례와 같이 2개의 정수와 연산자를 입력받은 후, Add, Sub, Mul, Div 중에서 이 연산을 처리할 수 있는 객체를 생성하고 setValue() 와 calculate()를 호출하여 그 결과 값을 화면에 출력하면 된다고 생각하였다. 철수처럼 프로그램을 작성하라.
두 정수와 연산자를 입력하시오 >> 57 + 12
9-1. 메인 클래스
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CalcMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
char sign = 0;
System.out.print("두 정수와 연산자를 입력하시오 >> ");
try {
a = scanner.nextInt();
sign = scanner.next().charAt(0);
b = scanner.nextInt();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("올바르지 않은 값 입니다. 다시 입력해주세요!");
}
Calc add = new Add(a, b);
Calc sub = new Sub(a, b);
Calc mul = new Mul(a, b);
Calc div = new Div(a, b);
switch (sign) {
case '+':
System.out.println(add.calculate());
break;
case '-':
System.out.println(sub.calculate());
break;
case '*':
System.out.println(mul.calculate());
break;
case '/':
System.out.println(div.calculate());
break;
}
scanner.close();
}
}9-2. Calc 클래스(상위이자 추상 클래스)
public abstract class Calc { // 추상 메소드 선언
public abstract void setValue(int a, int b);
public abstract int calculate();
}9-3. Add 클래스 (extends Cal)
public class Add extends Calc {
private int a, b;
public Add(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public void setValue(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public int calculate() {
return a + b;
}
}9-4. Sub 클래스 (extends Cal)
public class Sub extends Calc {
private int a, b;
public Sub(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public void setValue(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public int calculate() {
return a - b;
}
}9-5. Mul 클래스 (extends Cal)
public class Mul extends Calc {
private int a, b;
public Mul(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public void setValue(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public int calculate() {
return a * b;
}
}9-6. Div 클래스 (extends Cal)
public class Div extends Calc {
private int a, b;
public Div(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public void setValue(int a, int b) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
@Override
public int calculate() {
return a / b;
}
}10. 연습문제 7-22 번을 푸시오.
10-1. Circle 클래스
public class Circle extends Shape {
double r; // 반지름
@Override
double calcArea() {
return Math.PI * Math.pow(r, 2);
}
}10-2. Rectangle 클래스
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
double width, height; // 폭과 높이
@Override
double calcArea() {
return width * height;
}
boolean isSquare() { // 정사각형인지 아닌지를 알려준다.
boolean result = false;
if (width == height) { // 정사각형인지 아닌지의 판별식
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
return result;
}
}11. 연습문제 7-23 번을 푸시오.
11-1. Exercise7_23(메인 클래스)
public class Exercise7_23 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape[] arr = {new Circle(5.0), new Rectangle(3,4), new Circle(1)};
System.out.println("면적의 합 : " + sumArea(arr));
}
// 주어진 배열에 담긴 도형들의 넓이를 모두 더해서 반환
private static double sumArea(Shape[] arr) {
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i].calcArea();
}
return sum;
}
}11-2. 변경된 Circle 클래스
public class Circle extends Shape {
double r; // 반지름
public Circle(double r) {
this.r = r;
}
@Override double calcArea() {
return Math.PI * Math.pow(r, 2);
}
}11-3. 변경된 Rectangle 클래스
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
double width, height; // 폭과 높이
public Rectangle(int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
double calcArea() {
return width * height;
}
boolean isSquare() { // 정사각형인지 아닌지를 알려준다.
boolean result = false;
if (width == height) { // 정사각형인지 아닌지의 판별식
result = true;
} else {
result = false;
}
return result;
}
}'WebDev > 본과정' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Clone과 Wrapper 클래스 (0) | 2021.05.13 |
|---|---|
| 예외처리와 JVM 및 Object 클래스 (0) | 2021.05.13 |
| 객체 비교와 인터페이스 (0) | 2021.05.12 |
| 다형성과 오버라이딩 (0) | 2021.05.12 |
| 정렬 심화와 상속 (0) | 2021.05.12 |



최근댓글